We are exploring how adding more species of plants to a farm (increasing its above-ground biodiversity) affects the crop productivity and environmental effects of farming
Above-Ground Biodiversity in Context
- Native grasses and wildflower plantings can have beneficial effects on the farm
- These effects may include pollination, pest and weed control, soil carbon storage, better water-holding capacity, erosion control, prevention of nitrogen leaching, and soil restoration
How we look at above-ground biodiversity
We are investigating several ways to increase biodiversity along its farm edges, by planting:
- Vegetated swales and canals: which help improve the quality of stormwater runoff
- Native grasses: which attract local pollinators and provide habitat for ground-nesting mammals and birds
- Forbs: which attract local pollinators
- Hedgerows: which attract more pollinators, can be an extra source of income (if providing fruits, nuts or wood), and can help improve water and air quality
Featured Research Projects
- California wildflowers and native bees
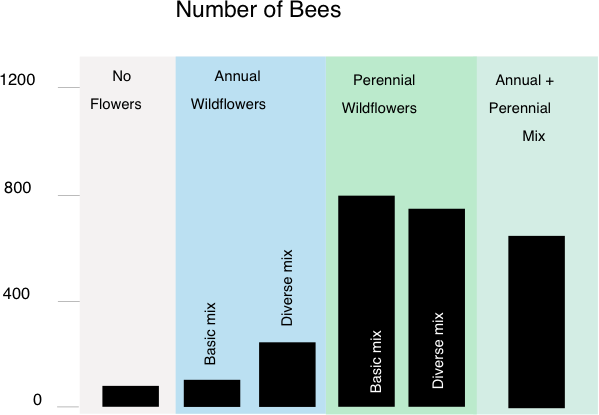 UC Davis researchers Neal Williams and Kimiora Ward are testing how different mixes of native California wildflowers attract native bees without attracting pests.
UC Davis researchers Neal Williams and Kimiora Ward are testing how different mixes of native California wildflowers attract native bees without attracting pests.
The researchers have found that wildflower mixes attracted up to ten times more native bees than control plots of typical weedy vegetation.
Ongoing work, started in 2010, is testing these wildflowers with different management systems at the Ranch to design methods that growers can use to successfully establish native wildflowers on their farms.
To learn more about this research, read the Williams’ lab’s 2015 article in Ecological Applications.
- Building milkweed habitat for monarch butterflies
- Coming soon
- Reintegrating sheep into vegetable cropping systems: first exploration of opportunities and challenges in CA
-
We are exploring the introduction of animal grazing in crop fields, a traditional agricultural practice around the world that has been replaced by modern farming methods. Our focal system is organic vegetable field crop, where we explore the potential of grazing to tackle challenges faced by managers of similar systems: loss of revenue during transition to organic, increased weed pressure, and suboptimal nutrient availability following cover crops. Our experiments include sheep grazing on winter cover crops.
This Integrated Crop Livestock System (ICLS) could have substantial economic, agronomic, and environmental benefits, including:
Added income from grazer conversion of cover crops to animal products
Non-chemical weed control
Increased gross primary productivity via cover crop regrowth
Improved soil nutrient availability for cash crops after grazing
Building of a healthy living that stores more carbon and reduce nutrient losses
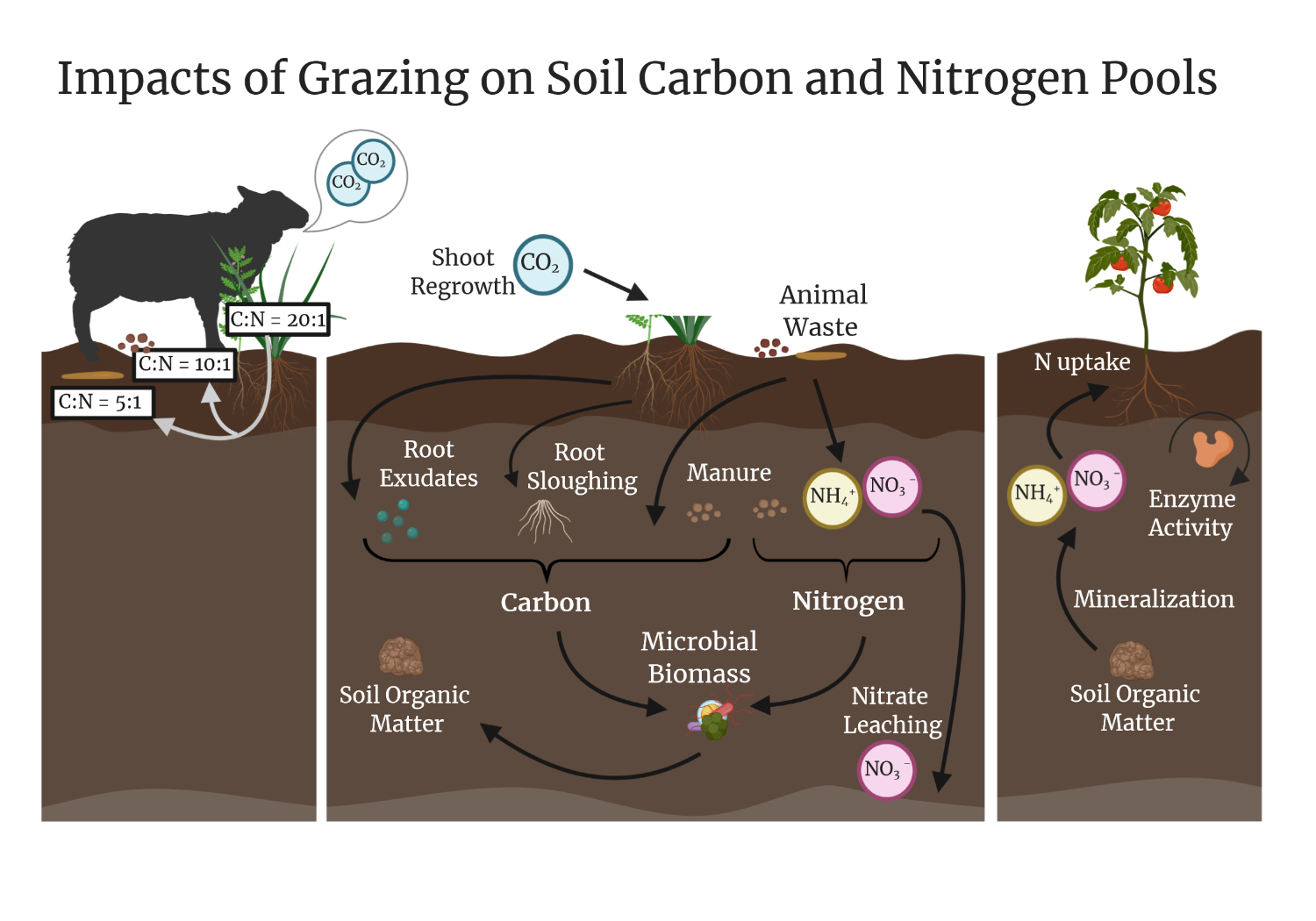
Figure by Sequoia Williams We currently have 2 studies investigating the impacts of spring sheep grazing of winter cover crops:
1. A grazing treatment on cover crops within a field in transition to organic farming. This trial explores how animal integration might help build soil carbon and nutrient stocks in support of a successful transition period, from an economic and agronomic perspective. We are simultaneously comparing annual rotational crops to the perennial legume alfalfa, with short-term grazing in both systems. Following the transition (summer 2022), tomato yields will be compared among all treatments.
2. Grazing integrated into a certified organic Corn-Tomato system, with comparisons between winter fallow, ungrazed cover crops and grazed cover crops (led by Amélie Gaudin’s agroecology group and Alda Pires). This trial focuses on measuring coupled changes in soil Carbon and Nitrogen pools, along with tomato and corn yields and potential food safety issues.
Timelapse of grazing on cover crops: start of grazing, end of grazing, regrowth, 10 days post-grazing